
Want to find out what is the secret behind finding the perfect balance of nutrients and texture in order to create the best soil for agriculture? Lets dig in!
Imagine the satisfaction of growing your own food, using the rich, fertile land beneath your feet. For many farmers, homesteaders, and agricultural enthusiasts, understanding soil types is the first step toward achieving a sustainable lifestyle.
In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the best soil for agriculture. You’ll discover the physical properties of soil, the soil triangle, and the pros and cons of different soil types. We’ll also cover how to manipulate your soil for better yields, the role of fertilizers, and the benefits of regenerative agriculture.
This Post Is All About The Best Soil For Agriculture
The Physical Properties of Soil
Texture and Composition
The texture of soil is determined by the size of its particles, which can be categorized into sand, silt, and clay.
Sandy soil has large particles that create ample space for air and water, promoting good aeration and quick drainage, but it offers low nutrient retention and may require frequent fertilization.
Clay soil has fine particles that compact tightly, retaining water and nutrients efficiently; however, this often leads to poor drainage and can make the soil heavy and hard to work with, especially when wet.
Silty soil falls somewhere in between, offering a balance of water retention and drainage capabilities. It has medium-sized particles that feel smooth and can hold nutrients better than sandy soil while providing better drainage than clay soil.
Each soil type has its own unique properties that affect plant growth and requires different management practices to optimize its benefits for gardening and agriculture.
Structure and Aggregates
Healthy soil consists of aggregates, which are clusters of soil particles bound together by organic matter and mineral particles. These aggregates improve water infiltration and root penetration, making it easier for plants to access essential nutrients and minerals. Furthermore, well-structured soil with good aggregate formation enhances soil aeration, promoting beneficial microbial activity.
Water-stable aggregates resist erosion and runoff, which is crucial for maintaining soil health and preventing the loss of topsoil. This stability also helps in retaining moisture, reducing the need for frequent irrigation, and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
The Soil Profile
The soil profile includes various layers, each playing a crucial role in supporting plant life. From the topsoil, rich in organic matter and teeming with microorganisms, to the subsoil where essential nutrients accumulate, every layer has its function. Beneath these, you might find the weathered parent material and the bedrock, which influence the soil’s properties.
A well-balanced soil profile contributes significantly to soil fertility, ensuring the availability of nutrients, and supports healthy plant growth by providing a stable environment for roots to expand. Understanding these layers is vital for effective soil management and sustainable agriculture.
The Soil Texture Triangle
Decoding the Triangle
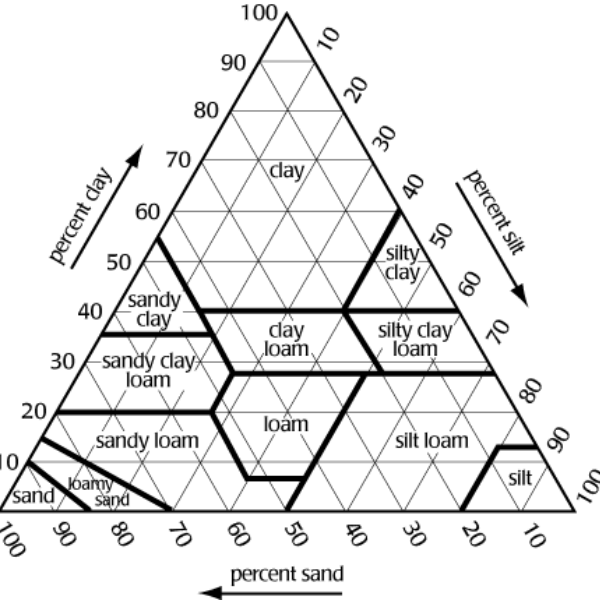
The soil texture triangle is a valuable tool used by soil scientists and agronomists to classify soil types based on their sand, silt, and clay content.
By plotting the percentages of these three components, you can accurately determine the soil type.
This classification helps in identifying various soil types such as sandy loam, which is known for good drainage and aeration, silty clay loam, which retains moisture and nutrients well, or loamy soil, which is considered ideal for plant growth due to its balanced texture and fertility.
Understanding soil texture is crucial for making informed decisions about agricultural practices, irrigation, and land management.
Practical Applications
Understanding your soil type helps in choosing the right crops and management practices, which can significantly impact your agricultural success.
For instance, loam soil, which is a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, is often considered the best type of soil for agriculture due to its high fertility and good drainage.
This type of soil allows for optimal root growth and water retention, ensuring that plants receive the nutrients and moisture they need to thrive. Knowing the characteristics of your soil can guide you in selecting crops that are well-suited to your environment and in implementing practices that enhance soil health and productivity.
Pros and Cons of Different Soil Types
Sandy Soil
- Pros:
- Excellent drainage
- Easy to work with
- Cons:
- Low nutrient retention
- Requires frequent watering
Clay Soil
- Pros:
- High nutrient retention
- Good water-holding capacity
- Cons:
- Poor drainage
- Hard to work when wet
Silty Soil
- Pros:
- Good nutrient retention
- Easy to compact
- Cons:
- Can become waterlogged
- Prone to erosion
Manipulating Your Soil for Better Results
Adjusting Soil Texture
Improving soil texture involves adding organic materials like compost or green manure to enhance its structure and fertility. For example, adding sand can improve drainage in clay soils, making them less prone to waterlogging and compaction.
On the other hand, incorporating compost into sandy soils can enhance nutrient retention and water-holding capacity, providing a more balanced environment for plant growth.
Regularly amending the soil with these organic materials can lead to healthier and more productive gardens and agricultural fields.
RELATED POST: How To Compost Cardboard: Best Cardboard Composting Guide
Enhancing Soil Structure
Practices like crop rotation and using cover crops can significantly improve soil structure over time.
Crop rotation helps by alternating the types of crops grown in a particular area, which can prevent soil depletion and reduce pests.
Using cover crops, such as clover or rye, can protect the soil from erosion and add vital nutrients when they decompose.
These methods increase soil organic matter and promote biological activity, including the proliferation of beneficial microorganisms, leading to more stable and resilient soil aggregates.
This enhanced soil health ultimately supports better crop yields and sustainable farming practices.
Addressing Soil Compaction
Soil compaction reduces root penetration and water infiltration. To alleviate this, avoid heavy machinery on wet soil and consider aeration techniques.
Best Soil For Agriculture
Loamy Soil
A balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, loamy soil is ideal for most crops. It offers good drainage, fertility, and root penetration, making it a preferred choice for gardeners and farmers alike.
The texture of loamy soil allows it to retain moisture and nutrients effectively while still providing sufficient aeration for plant roots, contributing to robust and healthy plant growth.
Alluvial Soil
Found in river valleys, alluvial soil is rich in nutrients and ideal for crop production. This fertile soil, deposited by rivers, contains a mix of sand, silt, and clay, which enhances its ability to retain moisture and nutrients.
It’s especially suited for vegetable farming, supporting the growth of a wide variety of crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens.
Organic Soil
High in organic matter, organic soil retains moisture and nutrients effectively, providing an ideal environment for plant roots to thrive.
This rich soil composition not only supports healthy plant growth but also improves soil structure, making it excellent for growing high-quality vegetables and fruits.
Additionally, organic soil promotes beneficial microbial activity, which further enhances nutrient availability and plant health.
DIY Soil Testing Techniques
Home-Based Soil Testing for Your Garden
Achieving a thriving home garden starts with understanding your soil. By employing simple, DIY soil testing methods, you can gain valuable insights into your soil’s nutrient composition and overall health.
Tools like home soil test kits and homemade pH tests provide you with the data needed for effective gardening. These easy-to-use methods allow you to identify nutrient imbalances and soil health issues, ensuring you can take the right steps to improve your garden’s productivity.
Essential Soil Testing Methods
pH Testing
Determining the pH level of your soil is crucial for understanding its acidity or alkalinity. You can use a simple pH testing kit, which typically includes a liquid reagent or test strips. These kits provide immediate results, helping you adjust soil conditions to suit the specific needs of your plants.
Nutrient Analysis
A comprehensive nutrient analysis will reveal the levels of essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in your soil. Many garden centres offer soil testing services, or you can send a sample to a professional laboratory. This detailed analysis allows for precise fertilizer recommendations to enhance soil fertility.
Soil Texture Test
Understanding soil texture is important for assessing its ability to retain water and nutrients. The jar test is a straightforward method: mix soil with water in a clear jar, shake vigorously, and allow the soil to settle into layers. The proportions of sand, silt, and clay layers will indicate your soil type, helping you amend it accordingly.
Organic Matter Content
Testing for organic matter content helps gauge the soil’s fertility and its capacity to support microbial life. Home compost testing kits can measure organic content, or you can send samples to a lab for more detailed analysis. High organic matter content is beneficial for plant growth and soil structure.
Electrical Conductivity (EC)
Electrical conductivity tests measure the soil’s ability to conduct electrical currents, which correlates with the soil’s salt levels and overall nutrient availability. Portable EC meters can be used in your garden to quickly assess soil salinity, ensuring you manage salt levels effectively to prevent plant stress.
Personalized Soil Fertility Plans
Creating a customized soil fertility plan for your home garden can significantly enhance plant growth.
With the information gathered from your DIY soil tests, you can develop a tailored fertility program that addresses specific nutrient deficiencies and improves soil structure.
This might include a balanced mix of compost, organic fertilizers, and natural soil amendments. By fine-tuning your soil’s nutrient profile, you ensure sustainable and healthy plant growth, turning your garden into a thriving oasis.
Fertilizers for Optimal Growth
Synthetic Fertilizers
While effective, synthetic fertilizer applications can lead to long-term soil degradation. They provide immediate nutrient boosts, which can enhance plant growth in the short term, but continuous use can harm soil health.
Over time, these fertilizers can reduce soil fertility, disrupt microbial communities, and increase dependency on further applications. Sustainable practices, like using organic fertilizers, beneficial bacteria, and crop rotation, can help mitigate these negative impacts.
Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers like compost and manure release nutrients slowly, providing a steady supply of essential elements to plants and improving soil fertility. These natural fertilizers enhance microbial activity, promoting a healthy soil ecosystem.
They are a sustainable alternative to synthetic options, reducing the risk of chemical runoff and contributing to long-term soil health. Additionally, the use of organic fertilizers supports the recycling of organic waste, further benefiting the environment.
Regenerative Agriculture and Soil Health
Leading the Way in Regenerative Agriculture: Advance AG
Nestled in the heart of Raymond, Alberta, Advance AG stands at the forefront of regenerative agriculture, championing innovative and sustainable farming practices.
With a mission to heal the land while maximizing crop yields, Advance AG focuses on soil health, diverse cropping systems, and reducing chemical dependencies. They offer a suite of services including soil testing, custom fertility programs, and crop consulting, utilizing cutting-edge technology to provide tailored solutions for each unique farm.
Their commitment to the environment and the community is reflected in their dedication to enhancing soil vitality, increasing biodiversity, and promoting practices that restore the natural ecosystem.
By integrating traditional knowledge with advanced methodologies, Advance AG is not only improving current agricultural outcomes but paving the way for future generations of farmers dedicated to sustainability and ecological stewardship.
The Role of Microbes
Microbes play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and biological nitrogen fixation, which improve soil fertility by converting atmospheric nitrogen into forms that plants can use. These microorganisms break down organic matter, releasing essential nutrients back into the soil.
Adding beneficial bacterial such as, Alive Elite or Alive Soil by Advance AG drastically improves microbial health.
Additionally, you can practice reduced tillage, which minimizes soil disturbance, and cover cropping, where crops are planted primarily to benefit soil health. This will further aid in promoting proper microbial health.
By fostering a healthy microbial ecosystem, these practices contribute to more sustainable and productive agricultural systems.
Carbon Sequestration
Regenerative agriculture techniques help in capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, storing it in the soil as organic carbon. This process not only enriches the soil by improving its fertility and water retention capacity but also combats climate change by reducing greenhouse gas levels.
Additionally, these practices support biodiversity and promote healthier ecosystems, leading to more sustainable farming methods and long-term agricultural productivity.
Water Management
Effective water management practices, such as water erosion control and improved water retention, are integral to regenerative agriculture.
These methods not only reduce soil loss but also enhance water quality by preventing pollutants from entering water bodies.
By implementing these practices, farmers can create more sustainable agricultural systems that support long-term soil health and productivity, ultimately leading to more resilient and environmentally friendly farming operations.
Case Studies from Advance AG
Potato Farming Success
Advance AG has demonstrated the benefits of healthy soil for potato farming. By focusing on soil health, they’ve achieved better yields and improved drought tolerance. More details can be found here.
Local Gardener’s Transformation
A local gardener in Alberta was shocked by the improvements in their garden after employing soil health techniques advocated by Advance AG. Their story highlights the value of sustainable soil practices. Read more here.
Innovative Drought Tolerance
Advance AG’s focus on soil biology has led to increased drought tolerance for various crops. Their success story showcases the importance of biological activity in soil management. Learn more here.
Growing Season and Environment in the Rocky Mountains
Gardening in the majestic backdrop of the Rocky Mountains presents unique challenges and rewards.
The growing season in this region is considerably shorter than in many other parts of the country, often lasting only from late May through early September. The altitude and cooler temperatures mean that every day counts in making the most of your garden.
Understanding the microclimates of your specific location within the Rockies can be the first step to success. Sunny, south-facing slopes will warm quicker in the spring and retain heat longer into the fall, providing a better environment for many crops.
Tips And Tricks For Rocky Mountain Gardening
Start Indoors:
To maximize the growing season, start your seeds indoors 6-8 weeks before the last expected frost date. Transferring well-established seedlings outside after the risk of frost has passed can give your plants a head start.
Choose Hardy Varieties:
Select plant varieties that are known for their hardiness and short growing periods. Root vegetables like carrots and radishes, as well as cold-tolerant greens such as kale and spinach, tend to thrive in the cooler mountain climate.
Use Season Extenders:
Employ season-extending tools such as cold frames, row covers, and hoop houses. These can protect your plants from unexpected frosts and help retain warmth, thus extending your growing season by several weeks.
Soil Preparation:
Rocky Mountain soil can be rocky and lean in organic matter. Amending your soil with plenty of compost and organic fertilizers will improve its structure and nutrient content. Raised beds filled with rich soil can also be a great option for mountain gardening.
Efficient Watering:
Due to variable precipitation and potentially dry conditions, it’s crucial to use efficient watering techniques. Drip irrigation systems can provide consistent moisture levels without wasting water. Mulching around your plants will also help retain soil moisture and reduce weed growth.
Wind Protection:
The mountain environment can be windy, which can stress young plants and reduce yields. Creating windbreaks using natural materials like logs or manufactured plastic screens can shield your garden from the harshest gusts.
Benefit from Companion Planting:
Incorporate companion planting strategies to repel pests and attract beneficial insects. For example, planting marigolds can deter aphids, while herbs like basil and thyme can attract pollinators.
By embracing these tips and tricks, you can turn the challenges of Rocky Mountain gardening into opportunities for growth and success. Whether you’re a seasoned homesteader or a newcomer to this rugged landscape, cultivating a thriving garden in the Rockies is a rewarding endeavour that connects you deeply with the natural world surrounding you.
Conclusion
Understanding the best soil for agriculture is essential for anyone looking to grow their own food sustainably. From recognizing the physical properties of soil to manipulating it for better yields, each step plays a vital role in achieving a successful harvest.
By choosing the right soil type, using appropriate fertilizers, and adopting regenerative agriculture practices, you can enhance soil health and support sustainable food production.
